
- 633
- 0
Parkinson’s Disease: Causes, Symptoms, Prevention, & Treatment
Parkinson’s disease is a neurodegenerative disorder that progressively affects movement and can significantly impact daily life. While there is currently no cure, understanding the causes, recognizing symptoms, and exploring prevention and treatment options are crucial aspects of managing this complex condition. In this blog, we’ll delve into the intricacies of Parkinson’s disease to provide valuable insights for patients, caregivers, and those seeking a deeper understanding.

Causes of Parkinson’s Disease:
The exact cause of Parkinson’s disease remains elusive, but both genetic and environmental factors are believed to contribute. Key factors include:
Genetic Predisposition:
- While the majority of cases are sporadic, a small percentage of individuals with a family history of Parkinson’s may have a genetic predisposition. Specific genetic mutations have been identified in some cases.
Environmental Factors:
- Certain environmental toxins, such as pesticides and herbicides, increase the risk of developing Parkinson’s disease. However, the relationship between environmental factors and the disease is complex and requires further research.
Age and Gender:
- Advancing age is a primary risk factor, with the majority of individuals being diagnosed after the age of 60. Men are also slightly more likely than women to develop Parkinson’s disease.
Symptoms of Parkinson’s Disease:
Parkinson’s disease manifests through a range of motor and non-motor symptoms. Some common indicators include:
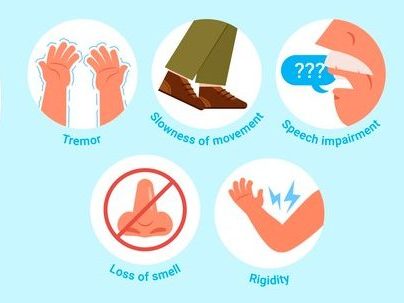
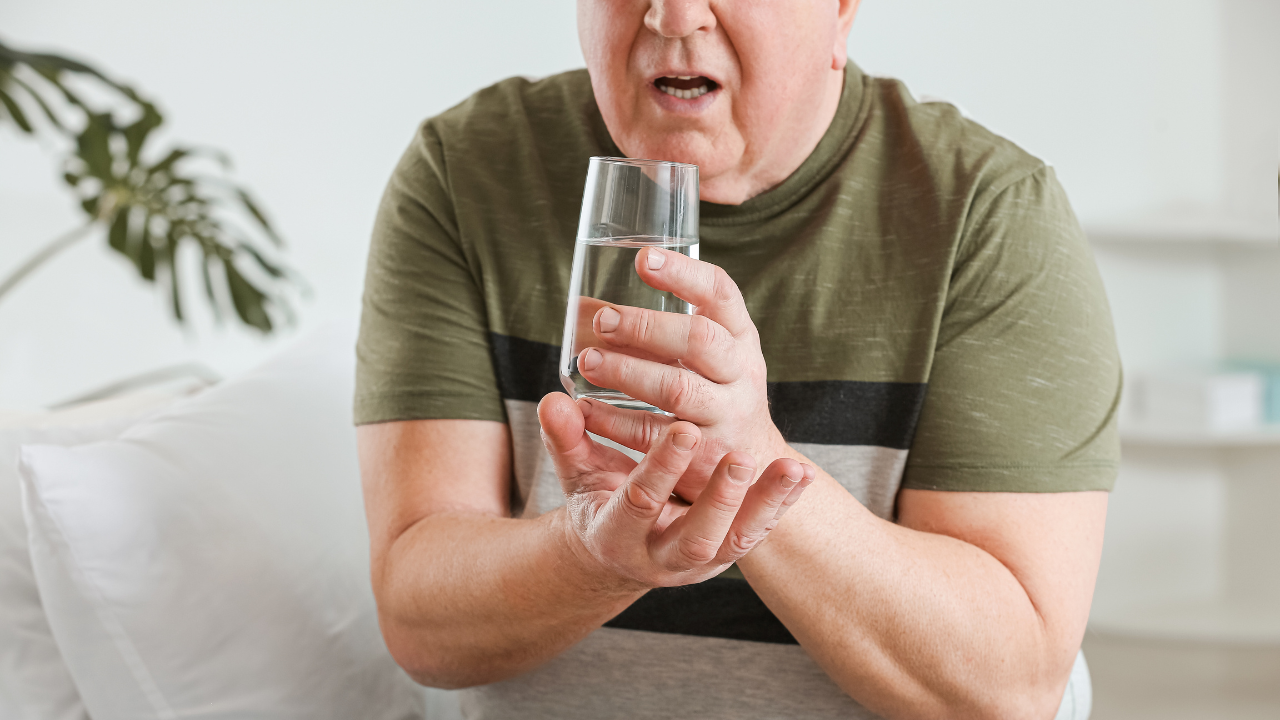
Tremors:
- Involuntary shaking or tremors, often starting in the hands, fingers, or limbs, are a hallmark symptom of Parkinson’s disease.
Bradykinesia:
- Bradykinesia refers to slowness of movement. Individuals may experience difficulty initiating or completing movements, leading to a gradual reduction in overall mobility.
Muscle Rigidity:
- Stiffness and tension in muscles, particularly in the arms and legs, can result in discomfort and reduced flexibility.

Postural Instability:
- Impaired balance and coordination may lead to difficulties in maintaining an upright posture and an increased risk of falls.
Changes in Handwriting:
- Known as micrographia, individuals with Parkinson’s may notice a progressive reduction in the size of their handwriting.
Prevention Strategies:
While we don’t fully understand the causes of Parkinson’s disease, adopting certain lifestyle choices may help reduce the risk of developing the condition:
Regular Exercise:
- Engaging in regular physical activity has been associated with a lower risk of Parkinson’s disease. Exercise promotes overall health and may have neuroprotective effects.
Get involved in regular activities with our MUKTI team:
Healthy Diet:
- A nutritious and well-balanced diet, rich in antioxidants and omega-3 fatty acids, may support brain health and potentially reduce the risk of neurodegenerative diseases.
Optimize your nutrition for both physical and mental well-being with assistance from our expert diet team:
Avoiding Environmental Toxins:
- Minimizing exposure to environmental toxins, such as pesticides and industrial chemicals, may contribute to a lower risk of Parkinson’s disease.
Cognitive Stimulation:
- Keeping the brain active and engaged through activities like puzzles, games, and lifelong learning may contribute to cognitive health.
Treatment Options:
While there is no cure for Parkinson’s disease, various treatment options aim to manage symptoms and improve quality of life:

Medications:
- Medications, such as levodopa, help replenish dopamine levels in the brain, alleviating motor symptoms. Other drugs, like dopamine agonists and MAO-B inhibitors, may also be prescribed.
Physical and Occupational Therapy:
- Physical therapy focuses on maintaining mobility and improving muscle strength, while occupational therapy addresses daily activities and functional independence.
Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS):
- In cases where medications alone are insufficient, DBS involves implanting electrodes in the brain to regulate abnormal electrical signals and improve symptoms.
Speech and Swallowing Therapy:
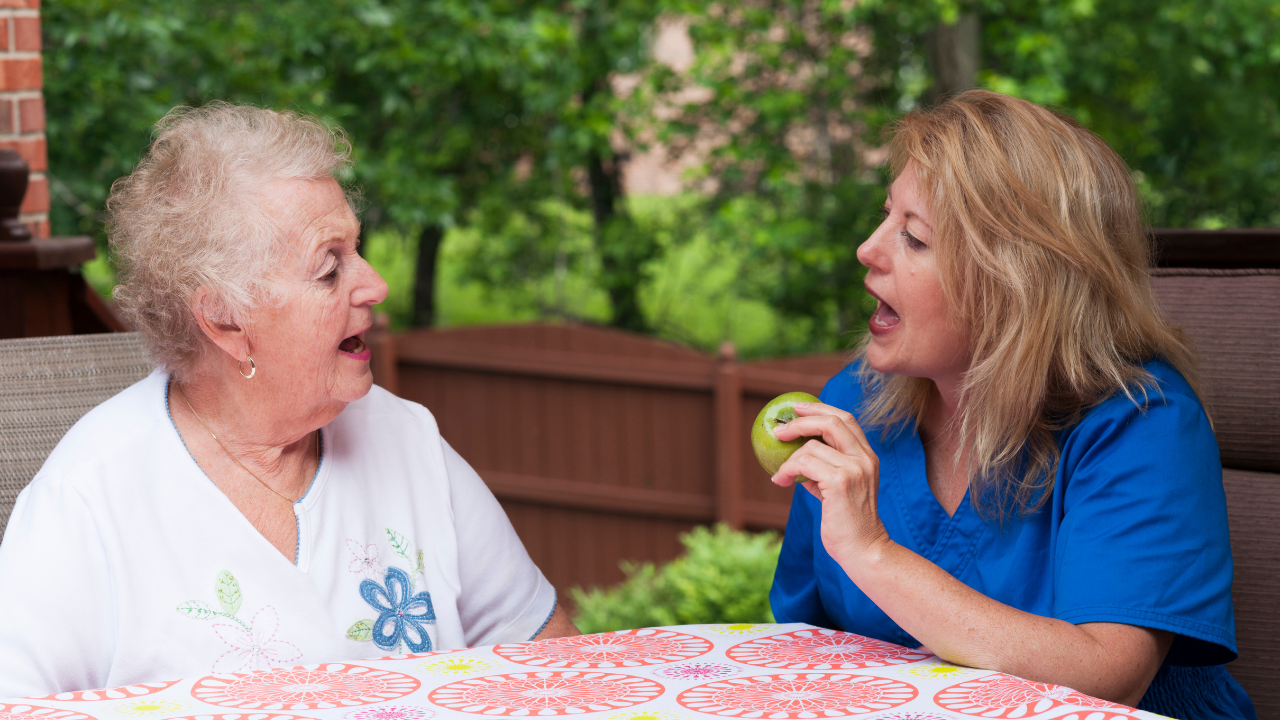

- Speech therapy can help manage speech and swallowing difficulties that may arise in later stages of Parkinson’s disease.
Parkinson’s is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder, and treatment primarily focuses on managing its symptoms and improving the quality of life for individuals affected by the condition.
Conclusion:
Navigating Parkinson’s disease requires a multidimensional approach that encompasses understanding its causes, recognizing symptoms, adopting preventive measures, and exploring available treatments. While the journey may present challenges, advancements in research and healthcare offer hope for improved management and quality of life for individuals with Parkinson’s and their families. By staying informed and fostering a collaborative relationship with healthcare professionals, those affected by Parkinson’s can better navigate the complexities of this condition and work towards a more fulfilling and empowered life.
Comment
Check Your EGFR
***We Promise, no spam!







