
- 575
- 0
Strategies for Living Well with Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disorder that primarily affects the joints, causing inflammation, pain, stiffness, and sometimes joint deformity. It’s a condition that can significantly impact a person’s quality of life. Understanding its causes, effects, symptoms, and available treatments is crucial for both patients and their caregivers.
The exact cause of rheumatoid arthritis remains unknown. However, researchers believe it’s a result of a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Certain genes, particularly those related to the immune system, may make some individuals more susceptible to developing RA. Environmental factors such as smoking, hormonal changes, and exposure to certain infections might trigger the autoimmune response in genetically predisposed individuals.
Some of the adverse effects of Rheumatoid Arthritis include:

- Joint Damage
- Bone Erosion
- Cardiovascular Complications
- Rheumatoid Nodules
- Fatigue
Understanding Secondary Amyloidosis in Rheumatoid Arthritis
In rheumatoid arthritis (RA), chronic inflammation and immune dysregulation can sometimes lead to secondary amyloidosis. This condition arises from the overproduction of serum amyloid A (SAA) protein. Elevated SAA levels increase the risk of amyloidosis development, where excess SAA proteins misfold and form amyloid fibrils. These fibrils deposit in organs like the kidneys, heart, liver, and spleen, causing dysfunction. Kidney involvement is a significant consequence, potentially leading to proteinuria, nephrotic syndrome, and kidney failure. Other organs may also be affected, resulting in complications such as cardiomyopathy and hepatomegaly. Early recognition of secondary amyloidosis is crucial for treatment decisions, focusing on controlling inflammation to reduce SAA production and considering therapies targeting amyloid fibrils to slow disease progression and preserve organ function.
Symptoms:
The symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis can vary from person to person and may come and go. Some common signs and symptoms include:
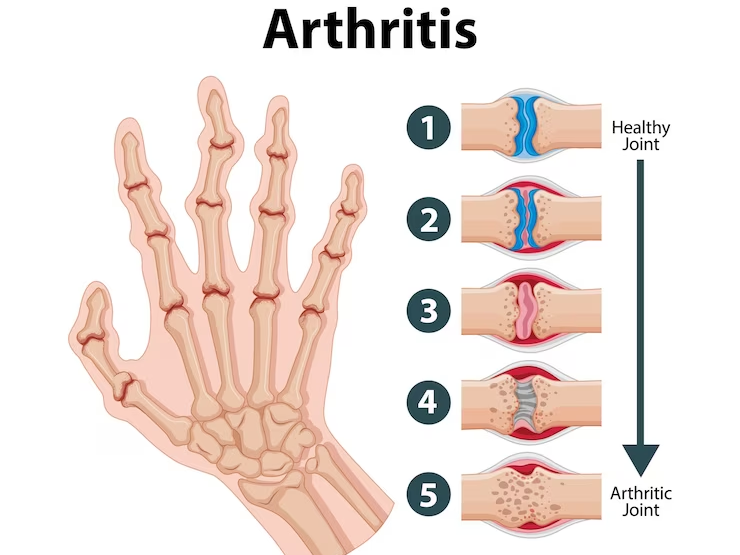
- Joint Pain and Stiffness
- Rheumatoid Nodules
- Joint Deformities
- Swelling and Tenderness
- Warmth and Redness
- Fatigue
- Fever
- Loss of Appetite
Treatments:
While there is no cure for rheumatoid arthritis, several treatments are available to manage symptoms, slow down the progression of the disease, and improve the quality of life for patients. These treatments include:
- Medications:
- Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs) to reduce pain and inflammation.
- Disease-modifying antirheumatic Drugs (DMARDs) to slow down the progression of RA and preserve joint function.
- Biologic Agents: Target specific components of the immune system to reduce inflammation and prevent joint damage.
- Corticosteroids: Provide short-term relief from inflammation and pain during RA flares.
- Physical Therapy: Exercises and physical therapy techniques can help improve joint function, flexibility, and strength.
- Surgery: In severe cases where joint damage is extensive, surgical interventions such as joint replacement may be necessary to restore function and reduce pain.
- Lifestyle Changes:
- Regular Exercise: Low-impact activities such as swimming, walking, and cycling can help improve joint mobility and reduce stiffness.
Physical activity stands as a potent remedy for Rheumatoid Arthritis. For further information, please reach out to us:
- Balanced Diet: A healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and omega-3 fatty acids can help reduce inflammation and manage RA symptoms.
You can also enrich yourself by joining our diet group:
Conclusion: Rheumatoid arthritis is a complex autoimmune disorder that affects millions of people worldwide. While it can be challenging to live with RA, advancements in medical treatments and therapies have significantly improved the outlook for patients. By understanding the causes, effects, symptoms, and available treatments for RA, individuals can better manage their condition and maintain a good quality of life. Early diagnosis and prompt intervention are key to effectively managing rheumatoid arthritis and minimizing its impact on daily life.
Comment
Check Your EGFR
***We Promise, no spam!







