- 1027
- 1
Hepatitis C and Kidney Disease: The Hidden Connection
Hepatitis C and kidney disease, both are very common and major medical complications throughout the world, although these two notorious villains are tangled with each other. The roles they play are interchangeable, anyone can be the cause and another can be the result of that.
So first we need to know what hepatitis is.
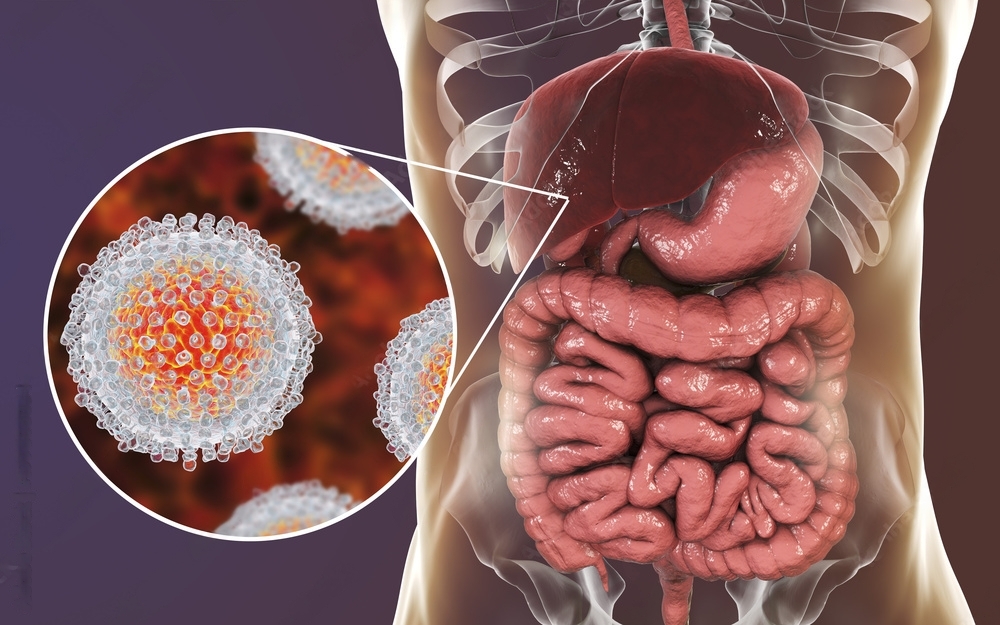
Hepatitis is the inflammation of the liver, mostly caused by viruses known as hepatitis A, B, C, D, and E. It can also be caused by drugs, alcohol, or genetic and immune problems.
How does Hepatitis C occur?
The hepatitis C virus is primarily transmitted through blood, with most infections resulting from exposure to contaminated blood due to unsafe injection practices, inadequate health care procedures, unscreened blood transfusions, injection drug use, and sexual activities that involve blood exposure.
Does All Types of Hepatitis Affect Our Kidneys?
Among the gang of viruses mostly hepatitis C is linked with kidney disease in addition to damage to the liver, musculoskeletal, immune system, hematopoietic system, and skin, and rare cases can lead to chronic kidney disease (CKD) or acute kidney injury (AKI).
Types of Hepatitis C Virus and why it is important to know the Genotype?
Hepatitis C has seven genotypes, numbered 1 through 7. In the Indian subcontinent, genotypes 1 and 3 are most common. Knowing your genotype is essential for managing chronic infections and developing future vaccines.
Who should go for the test?
All adults over 18 should be tested for chronic hepatitis C at least once. Annual tests for hematuria (blood in urine) and proteinuria (protein in urine) in HCV-infected patients can help detect kidney issues early.
How is Hepatitis C linked with CKD?
If you have chronic hepatitis C, it’s crucial to check your kidney function annually because:
- Hepatitis C can cause liver dysfunction, leading to insulin resistance, type 2 diabetes, and hyperlipidemia.
- These conditions can lead to kidney disease and kidney failure, as well as atherosclerosis and cardiovascular problems.
- Hepatitis C can trigger immune reactions that damage the kidneys, causing glomerulonephritis, where the kidney’s filters become inflamed and damaged, leading to CKD.
Does CKD develop immediately after Hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection?
No, not always. It may occur many years or even decades after HCV infection.
To check if your liver is healthy, please watch the video 👇👇

Clinical outcomes that indicate kidney disorders due to Hepatitis C Virus
- Nephritic Syndrome: Inflammation of the glomeruli, with symptoms like reduced urine output (oliguria), protein in urine (proteinuria), elevated blood urea nitrogen (BUN) and creatinine levels, cola-colored urine, and sometimes swelling (edema).
- Nephrotic Syndrome: Damage to glomeruli causing massive protein in urine (proteinuria), generalized swelling (edema), low blood albumin (hypoalbuminemia), and high blood lipids (hyperlipidemia).
To know more about the impact of kidney disease on liver health please click the blog below 👇👇

If you are a dialysis patient, you are at increased risk of getting Hepatitis C viral infection
Factors that induce HCV in dialysis patients –
- Contaminated equipment, medications, or other supplies
- Poor infection control practices
- Close proximity of dialysis patients
- Quick patient turnover between sessions
- Health status of patients
- Blood contamination of surfaces and devices
If you are a dialysis patient and also infected with Hepatitis C virus…
Your life is at risk and HCV impact on your survival. You will have an increased risk of cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma in the presence of HCV.
What happens if you are infected with HCV after Kidney Transplant?
- If you have HCV after a kidney transplant, your graft and patient survival rates are lower.
- You are at higher risk of developing new-onset diabetes mellitus after transplant (NODAT) due to immunosuppressants like steroids, tacrolimus, and cyclosporin.
- HCV increases the risk of liver complications, cardiovascular disease, and cancer, leading to higher mortality.
How does AKI occur from HCV?
- AKI, or acute kidney injury, happens when the kidneys suddenly stop working but can recover if the cause is treated.
- Rarely, HCV causes acute cryoglobulinemic vasculitis, affecting multiple organs, including the kidneys, lungs, skin, and nerves.
- Cryoglobulinemic vasculitis is an immune complex-mediated inflammation, injury, or necrosis of blood vessels.
Is there a vaccine for HCV?
Currently, there is no vaccine for hepatitis C. Therefore, proper management and avoiding behaviors that spread the disease are the best ways to prevent hepatitis C.
How to manage HCV in kidney disease (KDIGO Perspective):
- Before Kidney Transplant: Eradicating HCV is crucial to improve outcomes.
- After Kidney Transplant: Antiviral treatment is necessary if advanced fibrosis or severe cholestatic hepatitis develops.
The timing of treatment (before and after transplantation) should be determined by the nephrologist.
Other Treatment Options:
- Pangenotypic Direct-acting antivirals (DAAs) Monotherapy.
- Pegylated interferon and ribavirin for patients if they are resistant to DAAS.
Early intensive treatment of HCV can reduce the risk of death from liver, cardiovascular, cancer, and kidney diseases.
Conclusion
Hepatitis C presents a severe viral infection that can greatly affect kidney health. Consistent testing and suitable treatment are imperative for individuals with HCV to avert kidney disease and associated complications. Keeping abreast of information, undergoing testing, and adhering to medical guidance are essential steps to safeguarding your well-being.
Comment
Check Your EGFR
***We Promise, no spam!








2024-05-19 15:06:37
Surajit Chakraborti
Good presentation, matter appears complicated
Thank you for your feedback! We try to provide clear and comprehensive information. If any part seems complicated, please let us know, and we'll be happy to simplify or clarify it for you. Your understanding is our priority.